Power grid studies
Study of Earthing system
Context
The grounding network of an electrical installation has a crucial role in ensuring the safety of both people and equipment. The main functions of this buried grounding network are:
- Personal safty: Preventing electric shocks related to step and touch voltages (indirect contacts).
- Prevent equipment damage : Helping to distribute the ground potential rise to prevent overvoltages that could damage the equipment.
- Dissipation of lightning currents.
Requirement
Within the process of building a new electrical installation (such as a substation, delivery station, wind turbines, or a solar farm) or extending an existing site, implementing a grounding network is essential. Before starting to build, it is crucial to check that the planned grounding system complies with regulatory constraints. Therefore, a simulation-based analysis is necessary to validate its design.
Service overview
Capsim builds a model of the grounding network and of the soil using the XGSLAB software. This modeling enables :
- Validation of conductor section sizing.
- Calculation of step and touch voltages and comparison with required regulatory standards.
- Calculation of the overall impedance of the grounding network.
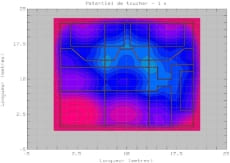
- Calculation of ground potential values and identification of the following zone boundaries (for the example a substation in France):
- 5000 V: Maximum allowable ground potential to prevent damage of the equipment inside the substation.
- 1500 V: Maximum allowable ground potential to avoid damaging third-party equipment.
- 650 V: Maximum allowable ground potential to protect telecommunication relays.
Results
The analysis validates the grounding network design and, when necessary, suggests modifications to ensure compliance with regulatory constraints. These adjustments may include adding a surface layer, installing grounding rods, or extending the grounding grid.
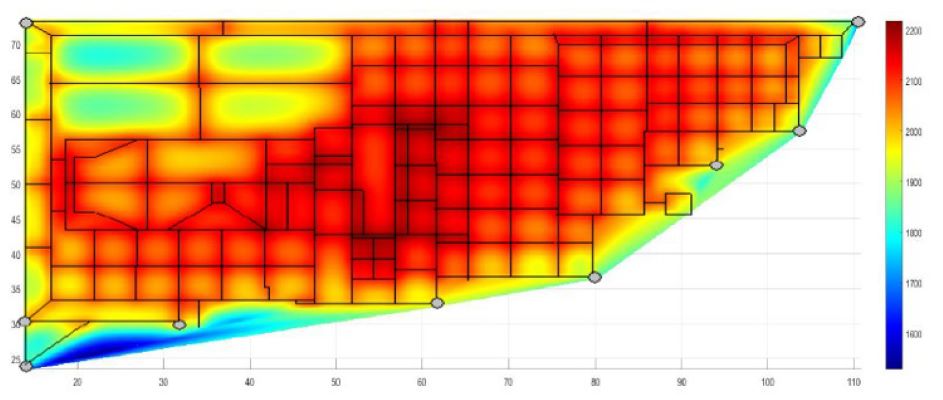
Touching voltage of a delivery station